Sensor Requirements
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
 |
±25V Voltage sensor User Guide What is included with the sensor, Sensor Specifications, Videos and experiment examples, Technical background, Maintenance and storage, and Warranty. |
*The following experiments include instructions for the Voltage sensor but they can also be used with the ±25V Voltage sensor.
|
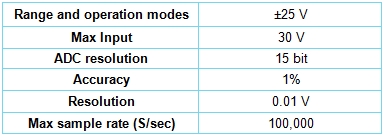
This sensor measures voltages across various resistive, capacitive and inductive components, as well as those of photovoltaic cells, batteries and power supplies. This sensor can also be used to measure electrode potentials and to investigate the charging and discharging of capacitors. When used in conjunction with the Current sensor, the dependence of the current flowing on the applied voltage can be studied in various electric circuits. This sensor can be used to measure low voltage AC and DC circuits. With its 4 mm plugs, it can easily be connected into electric circuits. |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
 |
ORP sensor User Guide What is included with the sensor, Sensor Specifications, Technical background, Maintenance and storage, and Warranty. |
|
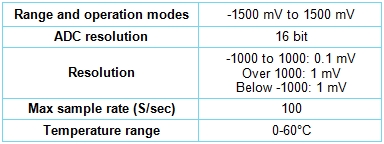
The NeuLog ORP (Oxidation Reduction Potential) sensor can be used to quantify whether a substance is a strong oxidizing agent or a strong reducing agent. For example, the ORP electrodes are used to measure the oxidizing ability of chlorine in swimming pools. The electrode has two components: a measuring half-cell comprised of platinum metal immersed in the solution in which the redox reaction is taking place, and a reference half-cell (sealed gel-filled Ag/AgCl) to which the platinum half-cell is referenced. |
 |
|
 |
 |
Bluetooth module BLT-202 |
 |
NeuLog Bluetooth & Battery All in One! |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|