Heat experiments
16/06/2025
The easiest way to see how simple it is to perform experiments with a logger sensor and how many possibilities it allows is to use the following set:
BLT-202 USB/Bluetooth communication module
NUL-203 Temperature logger sensor
Heat Transfer experiment video
This video provides a detailed overview of the NeuLog software – both online and offline modes – and demonstrates its versatile functions.
Latent Heat experiment video
This video explores temperature graphs of boiling water in a kettle and freezing water in a refrigerator using NeuLog sensors.
The lesson plan Latent heat experiment, can be found in Physics experiment page in this site.
The three classical phases of matter are solid, liquid and gas. Gas particles are well-separated whereas liquid particles are closer together. Solid particles are tightly packed, and are structurally rigid. The following figure describes the different types of phase changes:
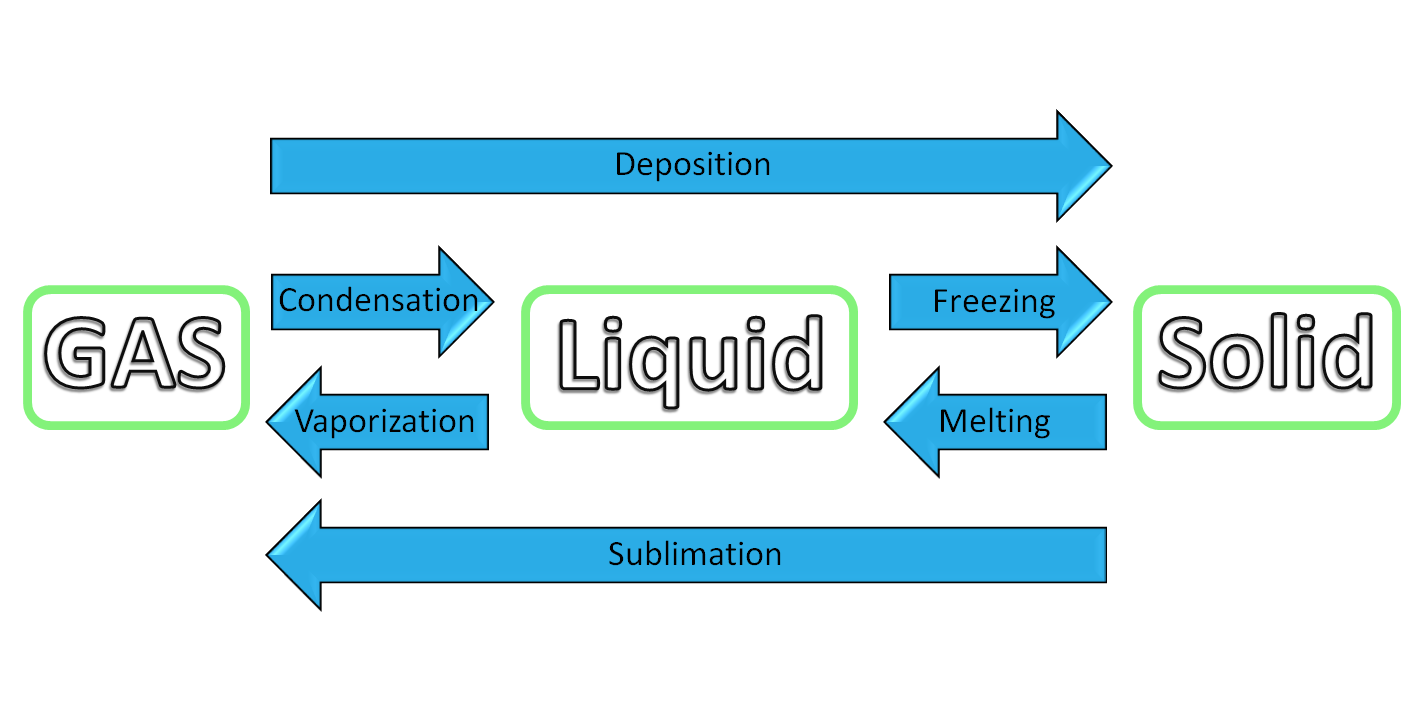
A heating or a cooling curve shows the change in temperature of a sample as it is heated or cooled. Sloped regions correspond to temperature changes in one of the different states. Flat regions (constant temperature) correspond to phase changes.
In this experiment we put the temperature probe in a kettle and see that while heating, the temperature stops rising at 100 Celsius degrees.
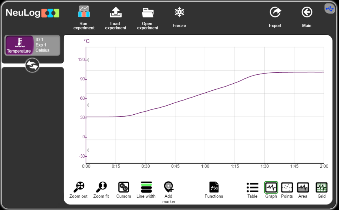
The reason for that is latent heat. Latent heat is the amount of energy absorbed or released by a substance during a change in its physical state (solid, liquid, gas) without a change in temperature.
In order to check the freezing state, we put the probe in a bottle with water and put the bottle in a freezer for 5 hours or more.
We can see that the temperature goes down and stays constant at 0 degrees Celsius. The temperature continues to go down when all the water has turned into ice.
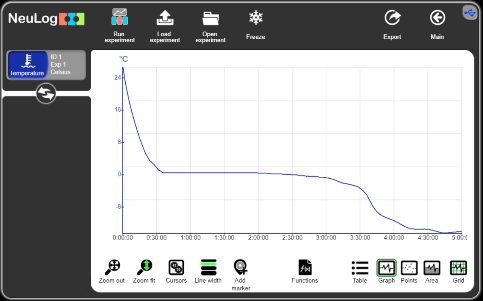
In this experiment we check also how salt affects the boiling and the freezing temperature points and to understand why we pour salt on icy roads.
The latent heat experiment is the fundamental for understanding distillation.
The lesson plan Distillation experiment, can be found in Physics experiment page in this site. This is an advanced experiment and requires a special kit for it.
Distillation is a purification method for liquids and separating liquid mixtures. It separates components of a mixture based on their boiling points (the temperature in which liquid changes into gas). It’s widely used both in laboratories and industrially, such as for refining crude oil or concentrating alcohol.
The general principle of distillation is starting with a mixture of liquids with different boiling points, heating the mixture to the first boiling point, cool down the vapor and collect the condensed liquid. This liquid is enriched with the lower boiling point component. The liquid that is left behind is enriched with the higher boiling point component.
In this experiment, we use a distillation kit to observe the distillation process by separating ethanol and food coloring from a solution.
More to read – NeuBlog
- Projects using NeuLog sensors and AI
- Basic Sound Set and Sound experiments
- Basic Motion Set and Motion experiments
- Basic pH Set and pH experiments
- Published Research with NeuLog GSR sensor
- Basic GSR Set and GSR experiments
- Basic Heat Set and Heat experiments
- Neuron Logger Sensors
- Coding For Young Students – The Next Big thing
- Most Beautiful Graphs in Physics
- Light sensor brought to light